An ingrown hair follicle is a skin condition that occurs when a newly grown hair curls backward and re-enters the skin. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and scarring. Ingrown hair follicles are common in areas where hair is shaved or waxed, such as the face, legs, and bikini line.
Ingrown hair follicles can be a nuisance, but they can also lead to more serious complications. If the ingrown hair follicle becomes infected, it can lead to an abscess or cellulitis. In rare cases, an ingrown hair follicle can even lead to scarring.
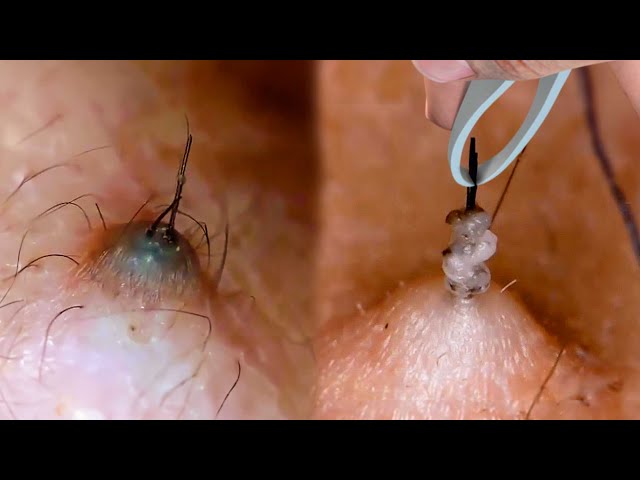
The first step in treating an ingrown hair follicle is to identify it. Ingrown hair follicles typically appear as small, red bumps that are tender to the touch. They may also be accompanied by pain, swelling, and itching.
Ingrown Hair Follicle
Ingrown hair follicles are a common skin condition that can occur when hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward. Understanding the essential aspects of ingrown hair follicles is important for effective prevention and treatment.
- Definition: A hair that grows inward instead of outward.
- Causes: Shaving, waxing, tight clothing, and genetics.
- Symptoms: Pain, redness, swelling, and itching.
- Treatment: Exfoliation, warm compresses, and topical antibiotics.
- Prevention: Shave in the direction of hair growth, use sharp razors, and exfoliate regularly.
In-grown hair follicles can be a nuisance, but they can also lead to more serious complications such as infection and scarring. By understanding the essential aspects of ingrown hair follicles, you can take steps to prevent and treat them effectively.
Definition
Ingrown hair follicles occur when hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including shaving, waxing, tight clothing, and genetics. Ingrown hairs can be painful, itchy, and unsightly, and they can also lead to infection.
- Direction of Hair Growth: Hair follicles naturally grow in a specific direction. When hair is shaved or waxed, it can be cut off at an angle, which can cause it to grow back into the skin.
- Sharpness of Razor: A dull razor can tug at hair and cause it to break off, which can also lead to ingrown hairs.
- Type of Hair: Coarse, curly hair is more likely to become ingrown than fine, straight hair.
- Skin Type: People with sensitive skin are more likely to experience ingrown hairs.
Ingrown hairs can be a nuisance, but they can also be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as folliculitis or hidradenitis suppurativa. If you experience frequent ingrown hairs, it is important to see a dermatologist to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Causes
Ingrown hair follicles are a common skin condition that can occur when hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward. There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of ingrown hair follicles, including shaving, waxing, tight clothing, and genetics.
- Shaving: Shaving can cause ingrown hairs because it cuts the hair off at a sharp angle, which can make it more likely to curl back into the skin. Shaving against the grain can also increase the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Waxing: Waxing can also cause ingrown hairs because it removes the hair from the root, which can make it more likely to grow back into the skin.
- Tight clothing: Tight clothing can rub against the skin and cause ingrown hairs. This is especially common in areas where the skin is thin, such as the underarms and groin.
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop ingrown hairs than others due to their genetics. This is because genetics can affect the shape of the hair follicle and the direction of hair growth.
Ingrown hair follicles can be a nuisance, but they can also lead to more serious complications, such as infection and scarring. If you experience frequent ingrown hairs, it is important to see a dermatologist to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms
Ingrown hairs can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, redness, swelling, and itching. These symptoms are caused by the hair follicle becoming inflamed and infected. The inflammation can cause the skin around the hair follicle to become red and swollen, and the infection can cause the area to become painful and itchy.
Ingrown hairs are a common problem, especially in people who shave or wax their hair. Shaving and waxing can cause the hair to be cut off at a sharp angle, which makes it more likely to curl back into the skin and become ingrown. Ingrown hairs can also be caused by wearing tight clothing, which can rub against the skin and irritate the hair follicles.
In most cases, ingrown hairs are not a serious problem and will resolve on their own within a few days. However, in some cases, ingrown hairs can become infected and may require medical treatment. If you have an ingrown hair that is causing you pain, redness, swelling, or itching, you should see a doctor to rule out infection.
Treatment
Ingrown hair follicles are a common skin condition that can occur when hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward. This can lead to pain, redness, swelling, and itching. There are a number of different treatments for ingrown hair follicles, including exfoliation, warm compresses, and topical antibiotics.
- Exfoliation: Exfoliation is the process of removing dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. This can help to prevent ingrown hairs by allowing the hair to grow out more easily. Exfoliation can be done with a variety of products, such as scrubs, loofahs, and washcloths.
- Warm compresses: Warm compresses can help to reduce inflammation and pain associated with ingrown hairs. They can also help to soften the skin and make it easier for the hair to grow out. Warm compresses can be made by soaking a washcloth in warm water and applying it to the affected area.
- Topical antibiotics: Topical antibiotics can help to prevent and treat infection associated with ingrown hairs. They are typically applied to the affected area twice a day.
In most cases, ingrown hairs can be treated at home with simple measures such as exfoliation, warm compresses, and topical antibiotics. However, in some cases, ingrown hairs may require more aggressive treatment, such as laser hair removal or surgery.
Prevention
Ingrown hairs are a common skin condition that can occur when hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward. This can lead to pain, redness, swelling, and itching. There are a number of different factors that can contribute to the development of ingrown hairs, including shaving, waxing, tight clothing, and genetics. However, one of the most important factors is shaving technique.
Shaving in the direction of hair growth helps to prevent ingrown hairs because it allows the hair to grow out more easily. When you shave against the grain, you are more likely to cut the hair off at a sharp angle, which can make it more likely to curl back into the skin. Using a sharp razor is also important because a dull razor can tug at the hair and cause it to break off, which can also lead to ingrown hairs.
Exfoliation is another important step in preventing ingrown hairs. Exfoliation removes dead skin cells from the surface of the skin, which can help to prevent the hair from becoming trapped under the skin. Exfoliation can be done with a variety of products, such as scrubs, loofahs, and washcloths.
By following these simple tips, you can help to prevent ingrown hairs and keep your skin looking its best.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section addresses common questions and concerns related to ingrown hair follicles, providing essential information for individuals seeking a better understanding of this skin condition.
Question 1: What causes ingrown hair follicles?
Answer: Ingrown hair follicles arise when hair grows inward instead of outward, commonly caused by factors like shaving, waxing, tight clothing, or genetic predisposition.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of ingrown hair follicles?
Answer: Ingrown hair follicles typically manifest as small, red bumps or pustules accompanied by discomfort, itching, and inflammation in the affected area.
Question 3: How can I prevent ingrown hair follicles?
Answer: Preventive measures include shaving in the direction of hair growth, using sharp razors, maintaining good skin hygiene by exfoliating regularly, and avoiding tight clothing that may induce friction.
Question 4: How are ingrown hair follicles treated?
Answer: Treatment options range from home remedies like warm compresses and exfoliation to medical interventions such as topical antibiotics, laser hair removal, or surgical extraction in severe cases.
Question 5: Can ingrown hair follicles lead to complications?
Answer: While generally not severe, ingrown hair follicles can occasionally lead to complications like infections or scarring. Seeking professional medical advice is advisable if symptoms persist or worsen.
Question 6: Who is at risk of developing ingrown hair follicles?
Answer: Individuals with coarse or curly hair, those who frequently shave or wax, and those with a family history of the condition are more susceptible to developing ingrown hair follicles.
These FAQs provide valuable insights into ingrown hair follicles, empowering individuals with the knowledge to effectively address and manage this common skin concern.
For further exploration, the following section delves into the specifics of treating ingrown hair follicles, offering practical guidance and insights into available treatment options.
Tips for Treating Ingrown Hair Follicles
The following tips can help you to treat and prevent ingrown hair follicles:
Tip 1: Exfoliate regularly to remove dead skin cells and help the hair to grow out more easily. You can use a gentle scrub or a washcloth with soap and water.
Tip 2: Apply a warm compress to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and pain. You can use a washcloth soaked in warm water or a heating pad set on low.
Tip 3: Use a topical antibiotic cream or ointment to help prevent and treat infection. Be sure to follow the directions on the package.
Tip 4: Avoid shaving or waxing the affected area until the ingrown hair has resolved. This will help to prevent further irritation and infection.
Tip 5: Wear loose-fitting clothing to avoid rubbing and irritation of the affected area.
Tip 6: See a doctor if the ingrown hair is severe, infected, or does not respond to home treatment. The doctor may need to remove the hair or prescribe medication.
By following these tips, you can help to treat and prevent ingrown hair follicles and keep your skin looking its best.
In conclusion, ingrown hair follicles are a common skin condition that can be treated and prevented with proper care. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to keep your skin healthy and free of ingrown hairs.
Conclusion
This article has explored the various aspects of ingrown hair follicles, from their causes and symptoms to their treatment and prevention. Key points to remember include:
- Ingrown hair follicles are a common skin condition that occurs when hair grows back into the skin instead of outward.
- They can be caused by a variety of factors, including shaving, waxing, tight clothing, and genetics.
- Ingrown hair follicles can be treated with home remedies such as exfoliation, warm compresses, and topical antibiotics. In severe cases, they may require medical treatment.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of ingrown hair follicles, you can take steps to prevent them and keep your skin healthy.
No comments:
Post a Comment